U.S. Embassy vs. Consulate: What EB-2 NIW Applicants Need to Know
Applying for a green card requires dealing with U.S. government agencies. If you are outside the U.S., you may need to visit a U.S. embassy or consulate. Many applicants struggle to understand the consulate-embassy difference. Especially when self petitioning for a green card.
This article explains embassies and consulates in simple terms. It also helps EB2 National Interest Waiver (NIW) applicants understand their roles in immigrant visa processing.
What is a U.S. Embassy?
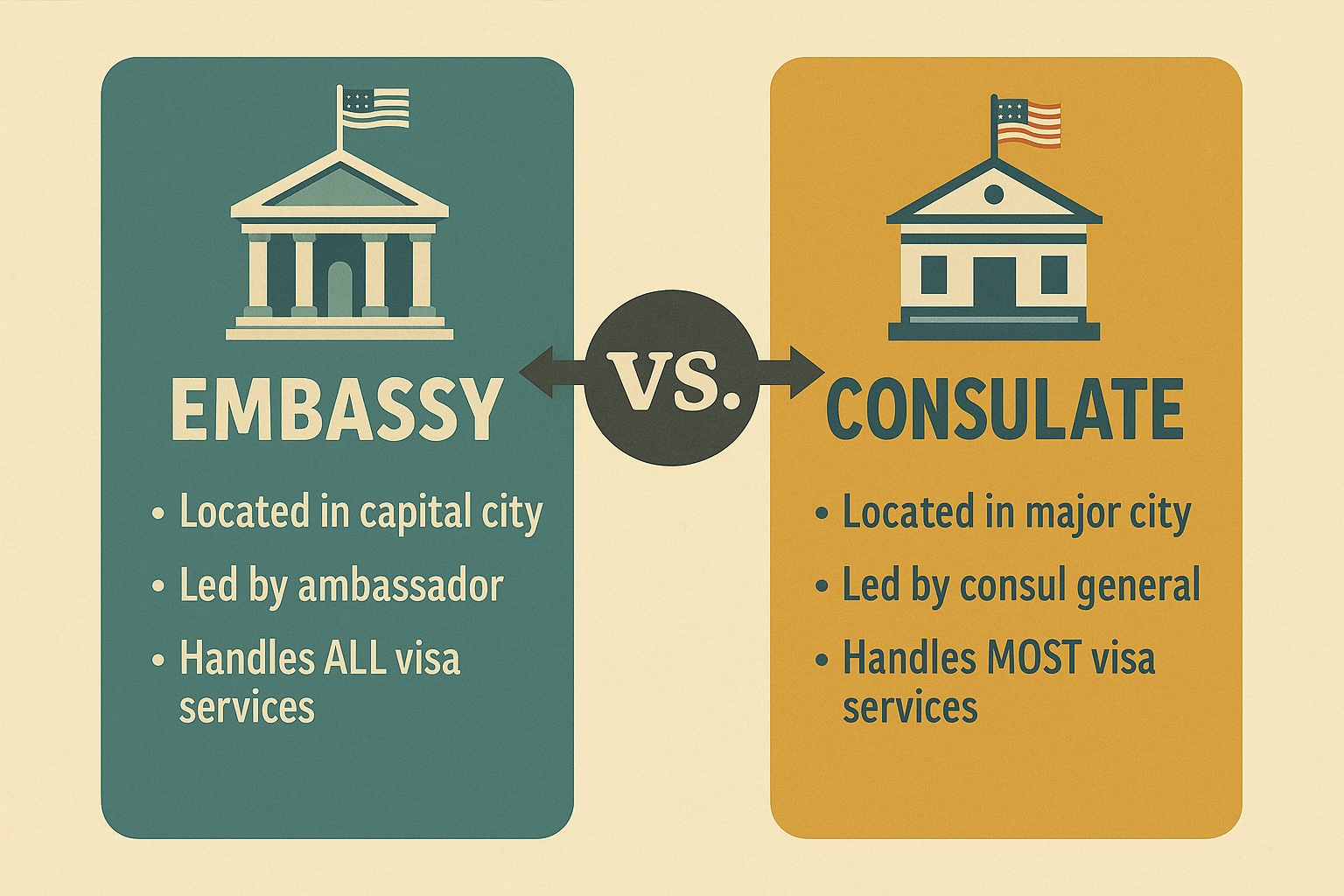
A U.S. embassy represents the U.S. government in a foreign country. This is the highest diplomatic office in that country. An ambassador oversees the embassy, which usually operates in the capital city.
The embassy manages diplomatic relations between the U.S. and the host country. It also handles U.S. foreign policy matters. Additionally, it provides assistance to U.S. citizens abroad.
The embassy processes immigrant visas and non-immigrant visas. This includes immigrant visas for approved NIW I 140 applicants. They must complete consular processing before becoming a lawful permanent resident in the United States.
It also oversees all consulates in that country. If a country has no U.S. consulate, the embassy manages all visa-related services.
Embassies play a crucial role in maintaining strong international relations. The ambassador is the head of the embassy. They work closely with foreign officials to negotiate treaties. They also discuss economic partnerships and ensure smooth diplomatic operations between both nations.
Moreover, they assist U.S. citizens living or traveling in that country. They handle emergencies and issue new passports. Additionally, they provide guidance in legal matters. The embassy serves as the main point of contact for diplomatic affairs.
What is a U.S. Consulate?
A U.S. consulate is a branch of the embassy. It operates in major cities outside the capital. A consul general leads it. Unlike embassies, consulates focus primarily on practical services rather than diplomatic relations.
Their main responsibilities include issuing visas, assisting U.S. citizens, and handling situations such as lost passports or travel disruptions. They play a crucial role in the immigration process. They manage most visa applications, including green card self sponsorship.
Consulates assist foreign nationals who want to travel to the U.S. They process applications for work, study, and tourist visas. For many applicants, the consulate is their first direct interaction with U.S. officials when seeking entry.
The interview, conducted at the consulate, determines whether you qualify for an immigrant visa. The consular officer evaluates documents, assesses the applicant’s background, and makes a decision based on U.S. immigration laws. If approved, this visa allows you to travel to the U.S. and complete the green card process.
While embassies and consulates both issue visas, the consulate is more accessible to people living outside the capital. If a country has multiple U.S. consulates, each serves a different region to make the process more efficient. However, if a country has no consulate, applicants must travel to the embassy to process their visa applications.
Difference between Embassy and Consulate
While both embassies and consulates serve U.S. interests abroad, they have different functions. Embassies handle high-level diplomatic relations, foreign policy discussions, and negotiations between governments. They also assist U.S. citizens abroad and provide visa services.
Consulates, on the other hand, focus on visa processing, assisting travelers, and handling local administrative matters. The main difference is in their scope.
Embassies handle a wide range of diplomatic affairs. Consulates focus mainly on consular services. These services include processing visas, assisting U.S. citizens abroad, handling legal matters, and providing emergency support for travelers.
Embassies are always in a country’s capital. Consulates operate in major cities. Because of this, embassies are usually larger, with multiple departments dedicated to foreign affairs, trade relations, and public diplomacy.
Embassies manage high-level diplomatic matters and foreign relations. Consulates primarily handle visa services. This includes the processing of immigrant visas for applicants with an approved EB2 NIW I 140 petition.
Why do NIW EB2 applicants need an Embassy or Consulate?
EB2 NIW allows applicants to self petition for a green card without an employer sponsor. EB2 falls under the employment-based visa categories. Because of this, applicants must prepare a strong petition letter package to showcase their expertise and national interest contributions.
After USCIS approves your NIW I 140 petition, the National Visa Center (NVC) receives your case. This occurs if you are applying from outside the United States. First, the NVC checks your application to ensure it includes all required information and fees. This step ensures your case is complete before moving forward.
Once processing is complete, NVC forwards your case to a U.S. embassy or consulate in your country. There, you will complete consular processing, including a visa interview.
You will receive an appointment notice with instructions on where to go for your interview. If your country has a consulate, your interview will likely take place there. If not, you must travel to the U.S. embassy.
Before the interview, you must complete a medical examination at a designated clinic. The exam ensures that you meet the health requirements set by U.S. immigration laws.
During the visa interview, a consular officer will ask about your background, work experience, and expertise. You must provide supporting documents. These include your passport, medical exam results, and proof of your national interest contributions. The officer will evaluate your case to decide if you meet visa requirements.
If the consular officer approves your application, you will receive an immigrant visa in your passport. This allows you to travel to the United States. Upon arrival, a U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer will admit you as a lawful permanent resident. USCIS will mail your green card to you after you enter the U.S. This marks the final step in your self sponsored green card process.
If you are already in the U.S., your case remains with USCIS, and you may apply for Adjustment of Status (Form I 485) instead.
Challenges in the consular process
Applying for a green card through a consulate or embassy comes with challenges. One major concern is processing time. Some embassies and consulates experience long wait times because of high demand.
Scheduling an interview can take weeks or even months. Applicants should check the current processing times at their designated location to plan accordingly.
Denials are another challenge for EB2 NIW self petition applicants. If the officer determines that the applicant does not meet the visa criteria, they may deny the visa.
In some cases, the officer may request additional documentation which can delay the entire process. Understanding U.S. immigration policies and preparing thoroughly can help improve the chances of approval.
Another issue is the availability of embassies and consulates. Some countries have limited U.S. diplomatic presence, forcing applicants to travel long distances. If an applicant’s home country does not have a U.S. embassy or consulate, they cannot process their visa there.
Instead, they must travel to another country for processing. This adds costs and logistical difficulties to the process.
Final thoughts
Understanding the consulate-embassy difference is crucial for self petition EB2 NIW green card applicants.
While both provide visa services, consulates handle most visa interviews. If U.S. immigration approves your NIW I 140 and you are outside the U.S, you must complete consular processing. Knowing the correct location saves you time and effort.
Before your interview, review all required documents and ensure they are complete. Research your specific embassy or consulate to understand their requirements. Be prepared to explain your work and how it serves the national interest of the U.S.
The visa process can be complex, but proper preparation makes a difference. Whether you visit an embassy or a consulate, understanding their roles is essential. This knowledge helps you navigate the final steps of your green card journey.
If you are ready for your interview, approach it with confidence and clarity. Wishing you success in your visa process.














